Clinical research & operations
Roll out more sites, faster, with the highest level of control over the outcomes
With thousands of clinical trials successfully rolled out at global level, Linguamatics experts have established a gold standard of translation for clinical documentation, which you now can access and implement. When you team up with Linguamatics, you leverage years of best practices, meaningful innovation and overall clinical expertise on the global stage.
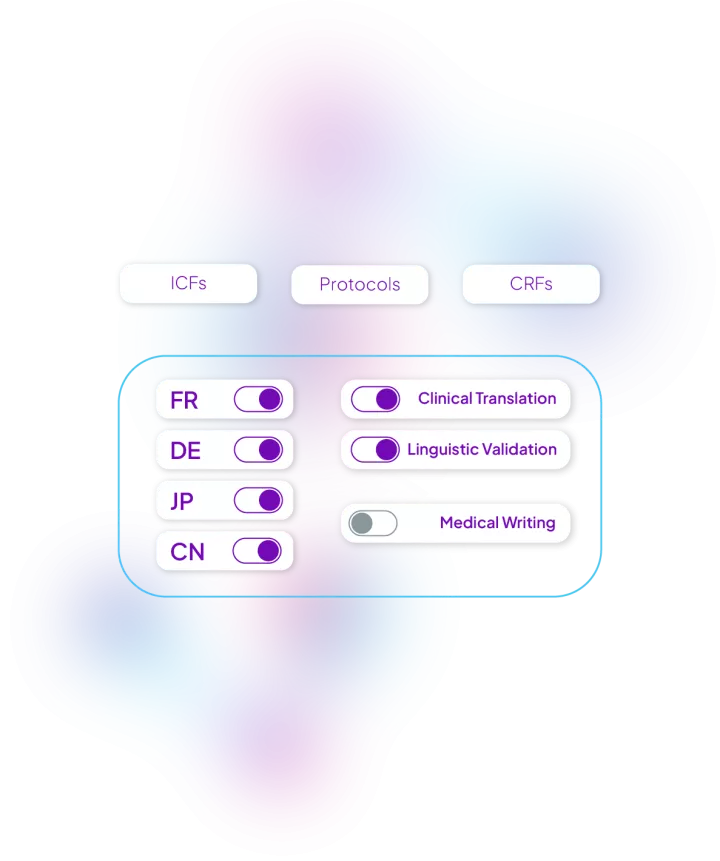
We built workflows for each type of clinical documentation to be localized in the quickest and most efficient way possible. Some examples of documentation we localize everyday in hundreds of languages:
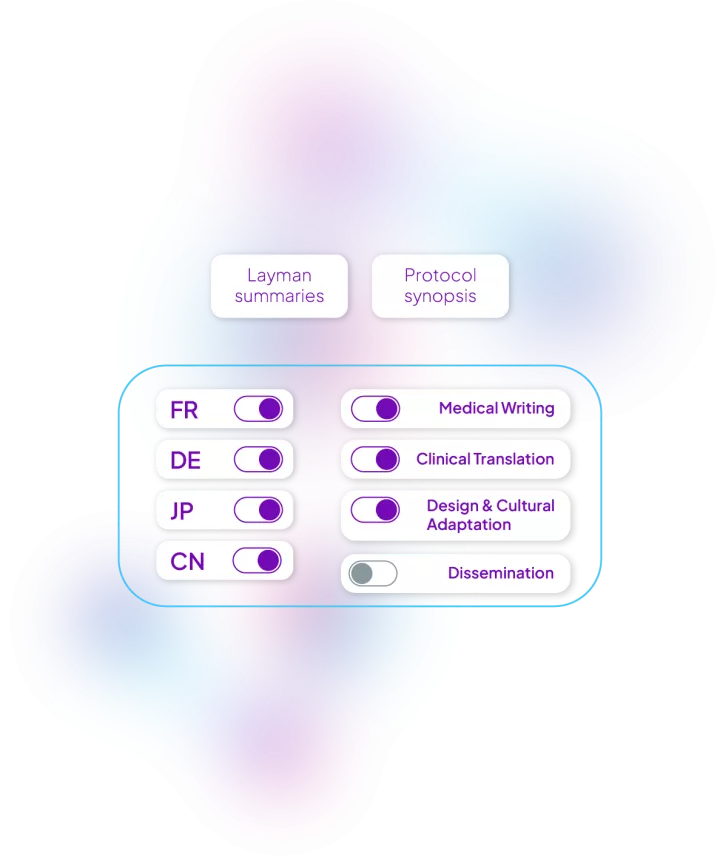
With the evolution of clinical trials and the desire to be more patient-centric and inclusive, we have designed an end-to-end solution to support protocol synopsis and layman summaries.
Our solution includes:
Linguamatics technology suite: Hub, Translate and NLP is the only language technology suite specifically created for life-sciences applications, with a major focus on Clinical documentation.
Linguamatics hub is our single-entry portal allowing portal submission or system integration for sending any clinical documents securely, and tracking of all ongoing projects and cost savings.
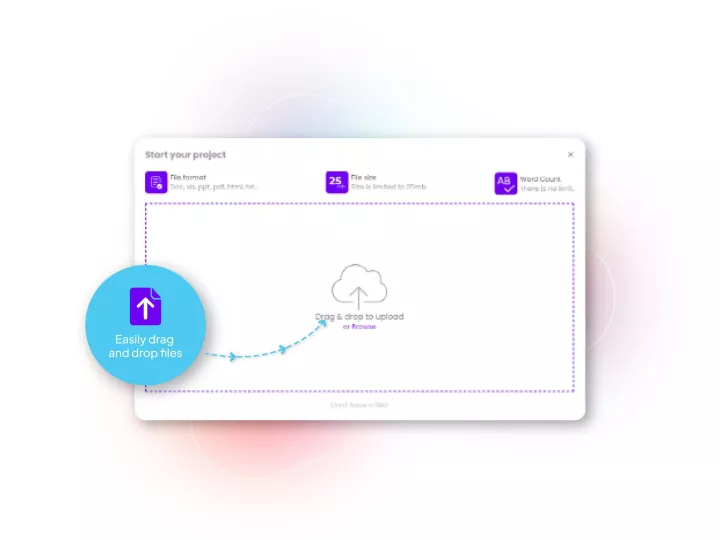
Linguamatics translate provides a unique analytics and machine translation technology trained for clinical documentation, allowing very fast handling, yet a high quality output in any language, which can then be certified by linguists and Subject Matter Experts. Access the best of AI and Human expertise in a single system.
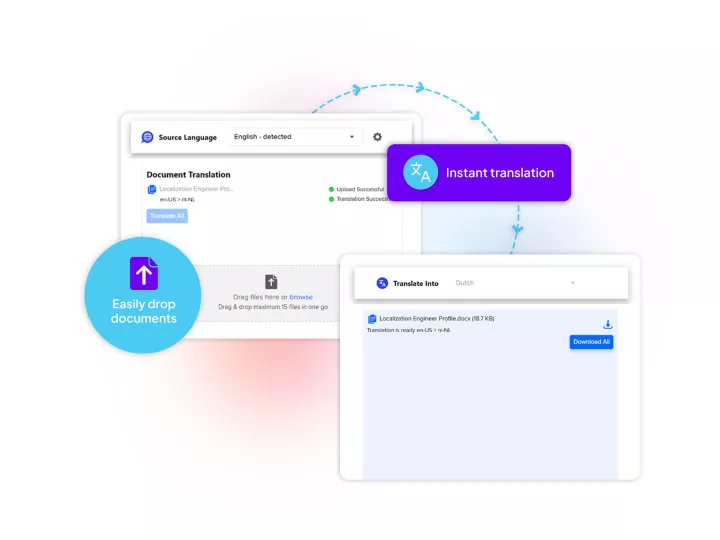
Linguamatics NLP is our award-winning NLP solution has been deployed across top pharma to optimize clinical trial protocol design, mine clinical trial reports, digitalize clinical trial protocols and more.
Our solution can be used over proprietary data and our content store with easy access to mine sources such as clinicaltrials.gov, Pubmed and more. With production grade accuracy and scalability our NLP has been cited in over 100 publications.
From the choice of COA instruments to the licensing management, all the way to the linguistic validation that ensures the validity of reported outcomes from different languages and cultures, a lot of time and money can be saved by leveraging a partner which provides an end-to-end service.
Check for licensing management, existing pre-translated libraries of COAs, integration into eCOA systems, as well as a thorough understanding of Linguistic Validation.
Account for all resources needing access to language capabilities, including outsourced resources. Productivity matters, and if those resources are utilized to correct language errors or navigate complex translation management systems, it quickly impacts length and cost of trials.
Working with clinical experts can help anticipate those details and save significant amounts of time and money throughout a clinical trial.
AI is inevitable, and if most clinical translations need to be certified, leveraging clinical AI translation can positively impact time to market as well as provide significant savings. Natural Language Processing can also help save time and money at multiple stages of trials, for instance in target identification.
Require AI systems designed and trained for Clinical documentation, the only guarantee that you will reap the rewards in efficiencies.
