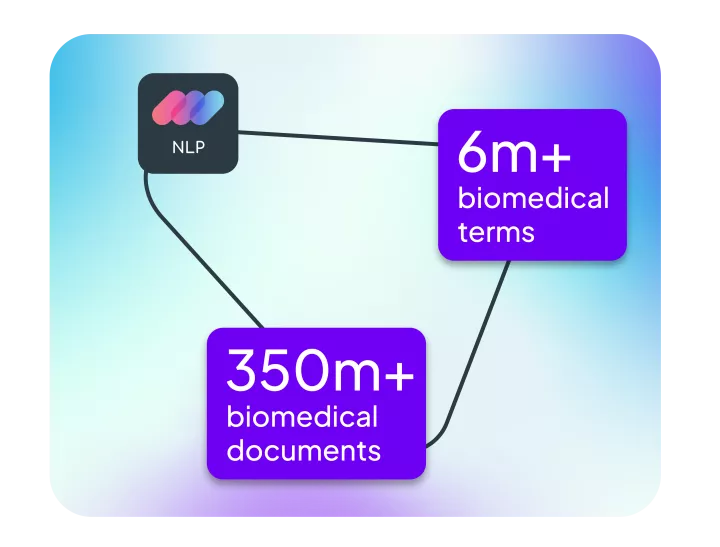
Linguamatics NLP
Transform text into positive healthcare outcomes
This list is not exhaustive but provides some of the things to consider when looking at AI and NLP solutions in healthcare. Linguamatics has been providing NLP solutions for over 20 years and would be happy to help you understand what tools would best solve your healthcare business challenges.